In November of 2014, UN secretary general, Ban Ki-Moon launched a new campaign in collaboration with the Guardian aimed at eradicating “female genital mutilation.” They announced this effort from Kenya’s capital city, Nairobi. Notably, their campaign occurred against the backdrop of a group of over 40 000 suspected Mau Mau rebels, who suffered torture under British colonial rule during the Kenyan Emergency (1952-1960), putting forward their claims to the UK High Court. These recent events in Kenya may seem unrelated but female genital mutilation and postcolonial struggles are in fact intimately and historically linked. This post looks at the history of the debate over clitoridectomy as it played out in Kenya between 1920 and 1960, in the midst of colonialism and decolonization.
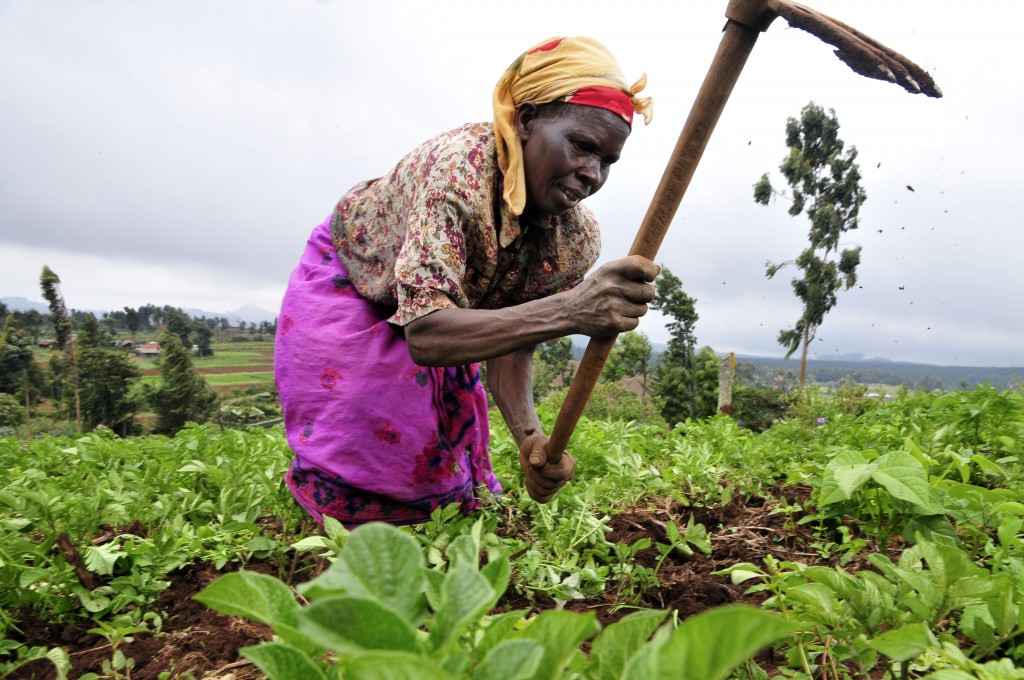

The history of Mau Mau begins in 1895, when the British established the East Africa Protectorate, with a view to exploiting the land, particularly in the western Highlands, for cash crop. Fertile and strategically valuable to British imperial interests, within twenty years, the Gikuyu people (also referred to as “Kikuyu”) who inhabited the Highlands were rapidly pushed out by white settlers. By 1950, the Gikuyu had lost 60 000 acres of land that belonged to themselves and their ancestors. They were confined to reserved areas or to “squatting” on European settler-owned farms. The land-squeeze engendered by the reservations left the Gikuyu with little choice but to embark on wage labour, whilst the “squatters” effectively entered into a pseudo-feudal relationship with white settlers, in which they held small plots of land in return for subsistence farming.
If this is the economic context of the Mau Mau uprising, it cannot be divorced from the socio-cultural context of Gikuyu configurations of female and male sexuality. Historians are in general agreement that land ownership was fundamental to Gikuyu conceptualizations of male adulthood – without land a Gikuyu male could not fully attain manhood. Yet the crisis that brought together issues of settler colonial exploitation, gender and sexuality took place around questions of female sexuality and womanhood. From 1929, the “Church of Scotland Mission to Kikuyu” began to ban from their schools children whose parents would not renounce clitoridectomy. The ban was the first in a series of broader attempts by the British government to denounce clitoridectomy as a “barbarous custom” and to eradicate it. The response from the Gikuyu was far from uniform, but opposition to the ban was considerable enough for many Gikuyu to form new schools that would allow the custom to be respected.
Until around the mid-1950s, imperial government attempts to regulate clitoridectomy were half-hearted with a view to treading carefully. In 1956, however, the Meru District governor declared “female circumcision” to be illegal in the district. In the midst of the violent protest over settler colonialism and land rights that became known as “Mau Mau,” this was a risky act from which the central government distanced itself. Yet its support by the Meru African District Council and the Njuri Ncheke (council of elders) revealed the tensions and fissures in Gikuyu society between those who collaborated with, and those who resisted, colonial rule. Almost immediately, in defiance of the ban, adolescent girls bought razor blades from local shops and went to the forests to circumcise themselves. In doing so, these girls, known as ngaitana (“I will circumcise myself”), were defying the authority of colonial-appointed chiefs and colonial rule itself. They and their families paid the price of that defiance – between 1956 and 1958, 2 500 people were charged before the African courts and fined in cattle, imprisoned or set to hard labour.
How, in the context of a renewed global effort to denounce clitoridectomy as “female genital mutilation,” are historians to understand the ngaitana’s act of self-circumcision and Gikuyu adherence to the practice more generally, even in the face of criminalization and punishment? Why did these girls choose to circumcise themselves despite debate about the dangers of the practice? There is no one, definitive answer to this question. Yet the fact that the re-assertion of the importance of this ritual passage to womanhood took place amongst the Gikuyu in the context of anti-colonial struggles for land and national independence is absolutely no coincidence.
For Jomo Kenyatta, the first president and nominal ‘father’ of independent Kenya, the rationale for clitoridectomy went to the very spiritual essence of nationhood. In Facing Mount Kenya (1938), effectively a manifesto of Gikuyu cultural nationhood, Kenyatta stated that clitoridectomy was “the conditio sine qua non of the whole teaching of tribal law, religion and morality.” For Kenyatta, representing the Gikuyu to itself and to the West, irua (female and male circumcision) lay at the heart of Gikuyu identity. Without it marriage, fertility, and thereby the continuation of the Gikuyu people, would be irredeemably threatened. Yet Kenyatta’s views on clitoridectomy were not always so forthright or un-ambivalent — in his earlier work he was pro-choice and possibly personally against the practice.
Post-colonial feminist scholars – I think rightly – read in Kenyatta’s text patriarchal nationalism’s need to control and appropriate female bodies as symbols of the nation. As Simon Gikandi has noted, Kenyatta, amongst other national figures including the Kenyan novelist, Ngugi Wa Thiong’o, were as much inventing as they were reflecting Gikuyu cultural identity. As missionary-educated young men in a world increasingly dominated by calls for national self-determination, they grappled with the pejorative stereotypes of African men as lazy, sexually promiscuous and ‘barbaric’ towards ‘their’ women – a sure marker of a lower stage of civilization. At the same time, they looked to community, tradition and cultural nationalism as a way of asserting difference from, and rejection of, Western racism and imperialism.
As Agnes Arnold-Forster notes, contemporary justifications for clitoridectomy focus on chastity, hygiene and female compliance to culturally specific forms of patriarchy. Often represented as “tradition” versus the incursion of Western “values,” these justifications fail to acknowledge the changeable and contextual nature of the meanings (and practices) of clitoridectomy. Kenyatta’s active support for, and countless Gikuyu girls’ participation in, a practice that has been denounced as “barbaric” for over a century cannot be divorced from colonial power relations or from the gendered limits of national self-imagining. Kenyatta was not configuring the meaning of clitoridectomy as part of irua in a vacuum, he was responding to the demands of colonial power to explain and legitimize Gikuyu existence in the patriarchal language of nationalism that ‘the West’ could understand. That is not to say that Kenyatta was necessarily a feminist or that Gikuyu society prior to colonialism was egalitarian. Rather, it is to argue that wider power relations – both economic and cultural – come together, inform and change the meaning of practices such as clitoridectomy. By looking at the debates around clitoridectomy in the context of colonialism in Western Kenya, it becomes possible to see just how historically embedded the meanings behind clitoridectomy are in power relations. This is not, of course, an argument for coerced mutilation of genitalia, rather it is an argument for understanding how the meaning of practices, even those that are painful and risky, are constantly changing in response to conjoined local and global dynamics of power.
Onni Gust is Assistant Professor of British Imperial history at the University of Nottingham. Onni researches and teaches on early nineteenth-century gender formation in the context of European imperial expansion, particularly in India.

NOTCHES: (re)marks on the history of sexuality is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Based on a work at www.notchesblog.com.
For permission to publish any NOTCHES post in whole or in part please contact the editors at NotchesBlog@gmail.com





I find it notably ironical that each time I read about FGM and the MAUMAU it is different but the gist is mostly the same not to argue on what has been stated but:
I am a kikuyu from the Mt.Kenya region and my great great grandfather was MAUMAU, my great grandmother was a child of only 12 yrs. I wish the past would be left alone for it is a painful time and considering that some powers in the world seem to never want as to forget about their authority…it’s like colonisation at a whole new level.
Thanks for commenting on the post and bringing in your own perspective. I fully appreciate that for yourself and others whose family and friends have been directly involved in the violent histories of empire, and for people who have themselves undergone FGM, these are emotionally difficult topics. I can see how to hear about them again and again is itself a form of violence.
Why don’t we just leave the past alone? As a historian of empire, as someone based in Britain who benefits from the white supremacy that imperial power engendered, I think it’s important to research and speak about the violence of imperial power if we are to understand how and why racism operates in Britain and the wider world today. Racist stereotypes and capitalist greed enabled a small group of white settlers to have their claims met above thousands of African people in Kenya. The violence of the colonial government was deemed acceptable at the time because white lives were deemed more precious that everybody else’s. These injustices continue in different ways across the world today and will continue unabated if we don’t resist them and, to my mind, part of that resistance comes about through an understanding and a retelling of history. I have no doubt that to do so is painful and in some ways violent (knowledge formation always is at a psychic level) but the other option is to leave history to the Niall Ferguson’s of the world, who continue to insist that white domination and imperial power is ultimately a good thing and the rest of the world need only copy what Europe did in the nineteenth century in order to advance.
An extremely interesting article. Despite the current view in the West that ‘the clitoris’ is the end-all and be-all of female genital pleasure, there are numerous examples that it is largely an organ – however small – that has taken on a symbolic value more than an actual one. Even ‘uncircumcised’ women do not use their clitoris as a light switch – if they don’t want to it stays desensitized (and in my experience it is pretty much that in many cases, women considering vaginal-anal sex as the normal way to connect with males). I didn’t know that some young women had performed clitoridectomies on themselves. I knew that the symbolic value had led some “Mau-Mau’ to circumcise a number of white females though.
There have to be something much deeper than ideaology to keep a movement moving towards it objectives
Circumcision of female in Kikuyu culture is a very “spiritual’. Practice , It was Nga’i Order to do That . It was not people’s choice .
You can never know the meaning unless you are a kikuyu and you have been taught the laws of Kikuyu (Kirira) .
We Kikuyu are very spiritual , but even you writing this you don’t have the idea .
Thayu Nyúmbá Ya Gikuyu